DecimateContinuous
Advanced Analysis Library Only
AnalysisLibErrType DecimateContinuous (double inputArray[], ssize_t numberOfElements, ssize_t decimatingFactor, int averaging, ssize_t startIndex, int initialize, ssize_t *decimatedLength);
Purpose
Continuously decimates the input sequence inputArray by the decimatingFactor and the averaging values that you specify. If Y represents the decimated output sequence, DecimateContinuous obtains the elements of the sequence Y using the following equation:
If averaging = 0 (off),
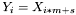
| for | i = 0, 1, 2, ..., size – 1 |
| size = ⌈(n–s/m)⌉ |
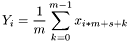
| for | i = 0, 1, 2, ..., size – 1 |
| size = ⌊(n–s/m)⌋ |
where n is the number of elements in inputArray, m is the decimatingFactor, s is the startIndex, size is the number of elements in the output sequence, ⌈⋅⌉ gives the smallest integer greater than or equal to the number, and ⌊⋅⌋ gives the largest integer less than or equal to the number.
Example Code
/* Compare the single decimate mode (Decimate) with continuous mode (DecimateContinuous). */
int nx, ny, ny1, segments[] = {2, 35, 43, 8, 19};
double *x1, *y1, *y2;
double *x, *y;
int DecFactor = 5, Avg = 0;
ssize_t startindex = 0, buffersize = 0, ny1_tmp = 0;
double avgsum = 0;
int i, j;
nx = 107;
ny = nx / DecFactor;
ny1 = (nx%DecFactor) ? (nx/DecFactor+1) : (nx/DecFactor);
printf("ny = %d\n", ny);
x = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double)*nx);
y = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double)*2*ny);
if (!x || ! y)
return OutOfMemErr;
y1 = y + ny;
y2 = y1;
WhiteNoise(nx, 1, 17, x);
Decimate(x, nx, DecFactor, Avg, y); //single mode
x1 = x;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){ //continuous mode
DecimateContinuous(x1, segments[i], DecFactor, Avg, startindex, ANALYSIS_FALSE, &ny1_tmp);
memcpy(y2, x1, ny1_tmp * sizeof(double));
x1 = x1 + segments[i]; //next input segment
y2 = y2 + ny1_tmp; //next output segment
}
free(x);
free(y);
Parameters
| Input | ||
| Name | Type | Description |
| numberOfElements | ssize_t | Number of elements in the input array. |
| decimatingFactor | ssize_t | Factor by which to decimate inputArray. decimatingFactor must be greater than 0 and less than numberOfElements. If decimatingFactor is greater than numberOfElements or less than or equal to zero, this function sets decimatingFactor to an empty array and returns an error. |
| averaging | int | Specifies whether to use averaging in decimating inputArray. Specify a nonzero value or select On in the function panel to specify that each output element is the mean of the decimatingFactor input points. Specify 0 or select in the function panel to specify not to average the output element. |
| startIndex | ssize_t | The index from which sample in inputArray the decimation starts if you call the function for the first time or initialize is a nonzero value. startIndex must be greater than or equal to zero. The default is 0. |
| initialize | int | Specifies whether to initialize the decimation. Specify a nonzero value or select Yes in the function panel to initialize the decimation from the startIndex of the input sequence. Specify 0 or select No in the function panel to resume the decimation from the previous sequence. To process a large data sequence that consists of smaller blocks, set initialize to a nonzero value for the first block and to 0 for all remaining blocks. You also can set initialize to a nonzero value at regular intervals of blocks to periodically reset the sample from which the decimation begins. |
| Output | ||
| Name | Type | Description |
| inputArray | double [] | On input, the input array to decimate. On output, this parameter returns the decimated sequence of inputArray. |
| decimatedLength | ssize_t | The length of the decimated sequence. |
Return Value
| Name | Type | Description |
| status | AnalysisLibErrType | A value that specifies the type of error that occurred. Refer to analysis.h for definitions of these constants. |
Additional Information
Library: Advanced Analysis Library
Include file: analysis.h
LabWindows/CVI compatibility: LabWindows/CVI 2012 and later